Why Anti-Static Grounding Straps Are a Critical Safety Feature for Hydrogen Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles
As the automotive industry pivots towards cleaner energy, hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) are emerging as a powerful and sustainable solution. However, with this innovative technology comes a unique set of safety considerations, particularly concerning the highly flammable nature of hydrogen gas. One of the most important yet often overlooked safety measures is the installation of anti-static grounding straps.
This article explores why these simple devices are not just a recommendation but a vital component for ensuring the safety of hydrogen-powered vehicles.
The Unique Risk: Hydrogen's Low Ignition Energy
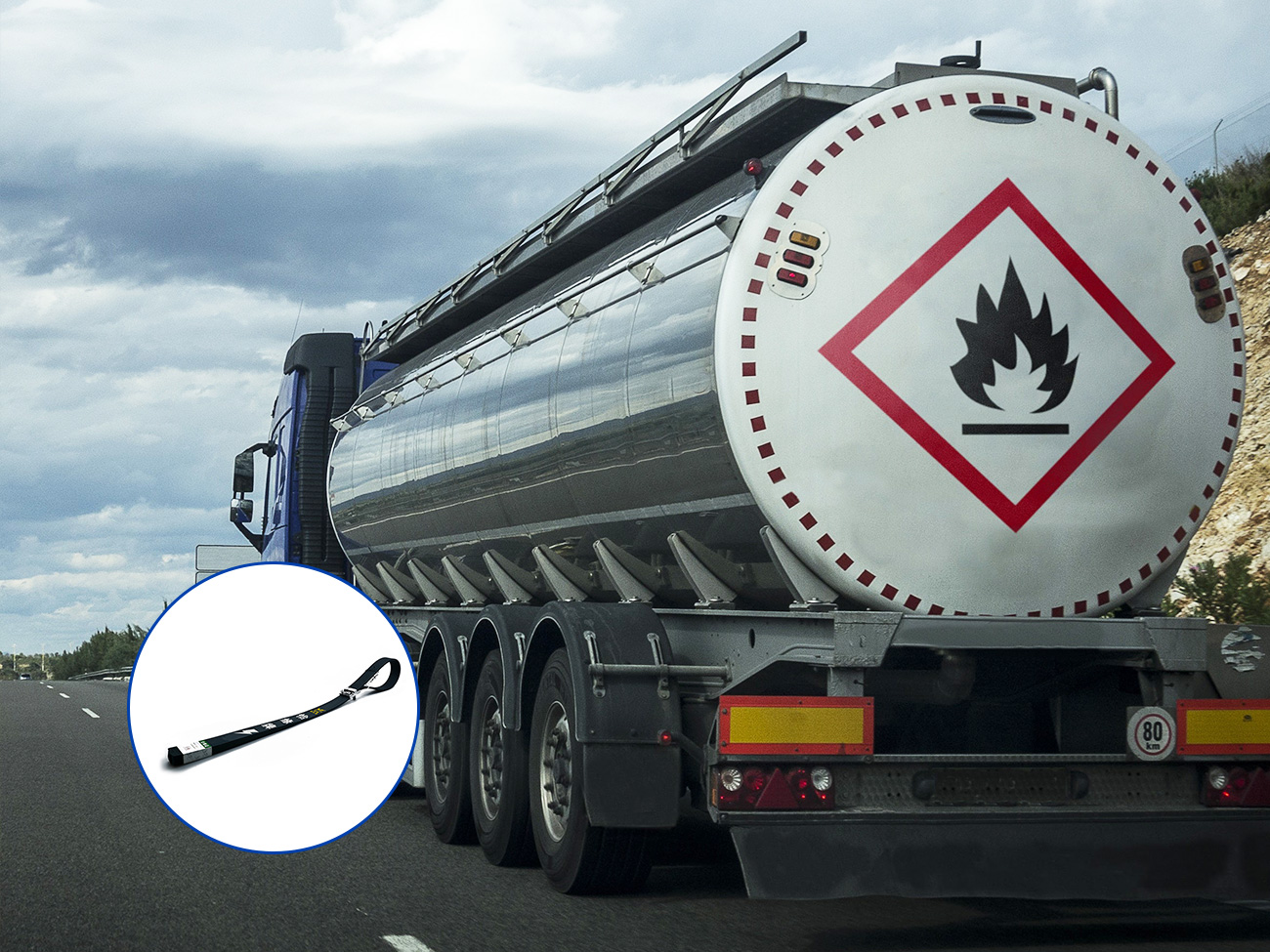
The primary reason anti-static grounding straps are crucial for FCEVs is the extremely low minimum ignition energy (MIE) of hydrogen gas. Compared to traditional gasoline, hydrogen requires a significantly smaller spark to ignite—a difference that can be the deciding factor between a minor static shock and a catastrophic incident.
During normal operation, a vehicle generates static electricity through various processes:
Friction: The vehicle's tires rolling on the road, air flowing over the body, and even fuel flowing through a hose can all generate static charges.
Insulation: The vehicle's rubber tires act as electrical insulators, preventing this static charge from dissipating into the ground.
This leads to a buildup of electrical charge on the vehicle's body, which, under the right conditions, can discharge as a spark. While this is generally harmless in a gasoline-powered car, in the presence of even a small hydrogen leak, that same spark could be an ignition source.
The Critical Moment: Refueling
The most hazardous time for static electricity is during the refueling process. Hydrogen fueling stations operate at high pressures, and the transfer of hydrogen from the dispenser to the vehicle's tank can create a risk of leaks. A static spark at this moment, particularly near the fueling nozzle or the vehicle's receptacle, could have devastating consequences.
For this reason, industry standards and best practices, such as those outlined in ISO 19880-1:2020, are very specific about grounding and bonding. These standards emphasize the need for a low-resistance path to true ground to prevent the buildup of electrostatic charge. While some fueling stations have their own grounding systems, a dedicated anti-static grounding strap on the vehicle provides an essential, continuous, and user-independent layer of protection.
The Solution: Continuous Static Dissipation
An anti-static grounding strap provides a continuous, low-resistance path from the vehicle's chassis to the ground. As the vehicle moves, the conductive strap drags along the road surface, ensuring that any static charge is immediately and safely discharged. This eliminates the risk of static buildup and the potential for a spark, both during driving and, most importantly, when the vehicle is stationary and being refueled.
For hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, these straps are a proactive safety measure that:
Mitigate Ignition Risk: They prevent the accumulation of static electricity that could ignite a hydrogen leak.
Enhance Refueling Safety: They ensure the vehicle is always grounded, complementing the safety protocols of a hydrogen fueling station.
Comply with Standards: They help vehicle owners meet the recommended safety guidelines for working with highly flammable gases.
The transition to hydrogen FCEVs represents a significant step towards a sustainable future. However, ensuring the safety of these vehicles is paramount. While complex engineering and safety systems are built into FCEVs, simple and robust solutions like anti-static grounding straps play a critical role in mitigating everyday risks. For any owner or operator of a hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicle, installing a high-quality, wear-resistant anti-static grounding strap is a straightforward, cost-effective, and essential step for protecting both the vehicle and its occupants.